- Understanding Ethical Hacking
- Ethical Hacking 1: Penetration Testing of a Corporate Network
- Ethical Hacking 2: Simulating a Social Engineering Attack
- Ethical Hacking 3: Assessing Web Application Vulnerabilities
- Ethical Hacking 4: Breaching Wireless Security
- Ethical Hacking 5: Detecting Insider Threats
- Conclusion
Ethical hacking is crucial in today's cybersecurity world, as it helps organizations identify and fix vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. Organizations are expected to spend over $300 billion on cybersecurity by 2024, with a significant portion going to ethical hacking services and penetration testing.
These statistics prove that ethical hacking plays a substantial role in today's cybersecurity landscape. In this article, we explore the world of ethical hacking through real-life examples. Each example discusses individual elements of ethical hacking, from penetration testing to social engineering, as well as ethical hacking tools, approaches, and tactics used by professionals in the field. We will also talk about the lessons learned from these scenarios and how they can be applied to improve security measures.
Whether you are a cybersecurity professional or an enthusiast, this article offers a deep dive into the practical application of ethical hacking that will surely help give you a clear understanding of this practice of using hacker techniques and methods.
Understanding Ethical Hacking
In the following sections, we will introduce you to the concept of ethical hacking, why ethical hacking is a vital cybersecurity practice that helps organizations protect themselves from the ever-growing threat of cyberattacks, the difference between ethical and malicious hacking, the ethical and legal standards, and the necessary skills of ethical hackers that play a crucial role in protecting the digital world.
What is Ethical Hacking?
Ethical hacking, also known as white-hat hacking, involves the authorized use of hacking techniques to identify vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks vulnerabilities, and applications that malicious hackers can exploit. Ethical hackers use the same techniques and ethical hacking tools as their malicious counterparts, but do so with the permission and approval of the organization being audited.
Ethical hacking aims to improve an organization's network security by finding weaknesses, reporting them, and proposing appropriate solutions and remediation measures. Ethical hacking analysis can include various activities, including network penetration testing, application security vulnerability assessment, social engineering simulations, and more. We will talk about these and other types of ethical hacking studies later. For now, let's learn about the importance and benefits of ethical hacking in cybersecurity.
The ideal solution for large-scale projects. Impeccable protection, high performance and flexible settings.
The Importance of Ethical Hacking in Cybersecurity
In today’s interconnected digital world, the danger of cyberattacks is constantly growing. Cyberattacks are becoming more targeted and sophisticated, making ethical hacking analyses especially important as they allows organizations to avoid these threats. Ethical hackers help prevent data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage by identifying and remediating security vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Regular ethical hacking assessments are also essential to maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture, as they ensure that defenses remain effective against new and emerging threats.
Renting our virtual private servers or virtual dedicated servers is a win-win option for creating a robust and secure digital infrastructure for your growing business.
Ethical Hacking vs. Malicious Hacking

While ethical and malicious hackers (commonly referred to as black-hat hackers) use similar methods, their goals are very different.
|
White-hat hackers aim to improve security by exploiting vulnerabilities and discovering and patching those same holes. |
Black-hat hackers exploit vulnerabilities for personal gain: stealing data, disrupting services, or demanding ransom. |
Certified ethical hackers operate under strict rules, have explicit permission from the organization, and are carefully monitored and documented to ensure that their actions comply with ethical and legal regulations, which we will discuss in the next section of the article.
Ethical Responsibilities and Legal Aspects
Ethical hacking comes with a lot of responsibility. Ethical hackers or white-hat hackers must follow a strict code of conduct to ensure their actions do not cause harm or violate any laws. Ethical responsibilities include:
- Getting explicit permission before conducting any tests.
- Clearly defining the scope of their work.
- Reporting all results to the organization without using them for personal gain.
In addition, ethical hackers must be aware of and comply with the relevant legal frameworks:
- Data protection regulations
- Computer crime laws
Ethical hackers must act within the law because any unauthorized hacking, even with good intentions, can lead to serious legal consequences.
Skills Required for Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking requires a diverse set of skills, such as:
- Technical knowledge
- Analytical thinking
- Problem-solving skills
Essential skills include a deep understanding of operating systems (OS), networking, and various programming languages and familiarity with penetration testing ethical hacking tools and techniques such as Nmap, Metasploit, and Wireshark. Since cybersecurity constantly changes, true hackers must stay up-to-date with the latest trends and threats. In addition, good communication skills are essential, as honest ethical hackers must clearly explain their findings and advice to technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Ethical Hacking 1: Penetration Testing of a Corporate Network

Scenario Overview
In this study, an ethical hacker was tasked with performing a penetration test on an extensive corporate network.
Objective: To assess the security vulnerability of its internal systems, discover potential vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
The network consisted of many vital assets, such as servers, databases, and workstations, each of which needed to be tested to ensure that it did not interfere with day-to-day operations.
Ethical Hacking Tools and Techniques Used
|
Research Phase |
Methods and Tools |
| Reconnaissance: Identifying potential entry points. |
Nmap for network mapping. Whois for collecting domain-related information. |
| Penetration testing. |
Metasploit for exploiting identified vulnerabilities. |
| Testing the strength of user credentials. |
Ripper and Hydra for password cracking. |
| Network traffic analysis. |
Wireshark to detect any unsecured data transmissions. |
| Testing employee awareness and response to potential threats. |
Social engineering attacks, such as phishing, to assess the human factor of security in the organization. |
Results and Lessons Learned
Using ethical hacking such as penetration testing, the following vulnerabilities were identified, and solutions were quickly provided to fix them.
|
Identified Vulnerabilities |
Steps to Fix Vulnerabilities |
| Outdated software with known exploits. |
Patch the software. |
| Weak password policies. |
Implement more robust password policies. |
| Unencrypted sensitive data transmitted over the network. |
Implement encryption for sensitive data. |
| Need for better employee training. |
A comprehensive cybersecurity awareness program was launched to educate employees on phishing and other common threats. |
Conclusion: Conducting regular penetration tests is critical to identifying hidden vulnerabilities, strengthening an organization's technical defenses, and increasing employee awareness.
Ethical Hacking 2: Simulating a Social Engineering Attack

Scenario Overview
In this case study, a company hired an ethical hacker to conduct a simulated social engineering attack to determine its employees' susceptibility to psychological manipulation techniques.
Objective: To determine how easy it was to trick employees into revealing sensitive data or taking actions that could jeopardize the organization's security. The test was conducted without prior warning to the staff to ensure adequate responses.
Psychological Manipulation Techniques
The ethical hacker used several social engineering tactics:
|
Method |
Description |
| Phishing |
Employees were sent carefully crafted emails that appeared to originate from reputable internal sources, such as HR or IT support. These emails asked employees to enter sensitive data, such as login credentials, or click on malicious links. |
| Pretext |
Ethical hacker called employees posing as senior managers or technical support agents. To create a sense of urgency, ethical hacker convinced employees to act immediately to prevent a perceived crisis. |
| Physical Social Engineering |
Ethical hacker posed as a courier to gain physical access to secure areas of the organization. Once in place, ethical hacker intended to collect data or install USB drives containing malware. |
Results and Mitigation Strategies
The social engineering attack simulation showed that many employees were vulnerable to social engineering attacks. The results of the social engineering attack simulation and the corresponding mitigation strategies are listed below:
|
Results |
Mitigation Strategies |
| Around 30% of phishing emails resulted in employees clicking on malicious links or sharing sensitive information. |
Regular phishing simulations were introduced. |
| Several employees provided sensitive information over the phone during pretexting attempts. |
A comprehensive cybersecurity awareness program was launched, focusing on educating employees on the dangers of social engineering and how to recognize such attacks. |
| The hacker successfully gained unauthorized physical access to the office. |
The organization also improved its physical security protocols, such as tighter access controls and employee screening procedures. |
Conclusion: Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. Therefore, ongoing employee training and awareness are essential to mitigate these threats and ensure that staff are the first line of defense against potential attacks.
Ethical Hacking 3: Assessing Web Application Vulnerabilities
Scenario Overview
In this example, an ethical hacker was hired to perform a vulnerability assessment of a web application used by a financial company. Given the critical nature of the data (sensitive customer information: personal data and financial transactions) handled by the application, the company wanted to ensure that it was protected from potential cyberattacks.
Objective: Identify and exploit any vulnerabilities in the application and provide recommendations on how to secure it.
Identify and Exploit Common Vulnerabilities
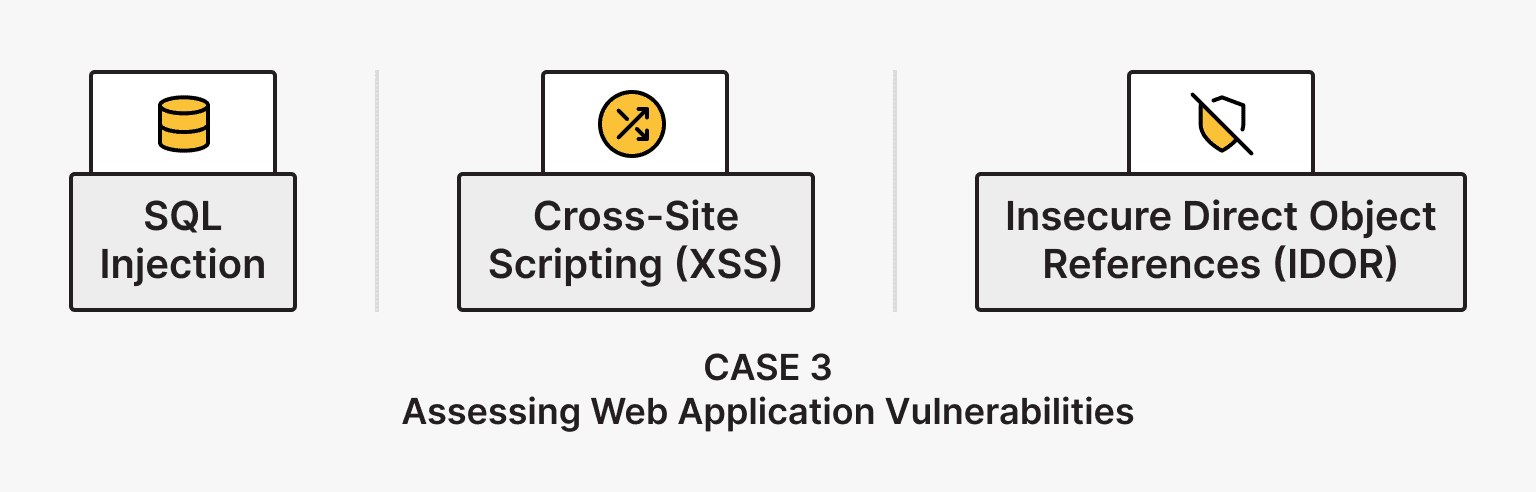
During Ethical Hacking 3, the following automated ethical hacking tools were used to scan the vulnerability of web applications: OWASP ZAP and Burp Suite, several vulnerabilities and their exploitation options were identified:
|
Identified Vulnerabilities |
Vulnerability Exploitation |
| SQL Injection |
Allowed hackers to manipulate the database by creating malicious SQL queries, which could lead to unauthorized access to customer data. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) |
Facilitated the injection of malicious scripts into applications that could be executed in users’ browsers, potentially leading to data theft or session hijacking. |
| Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR) |
Facilitated access to unauthorized records by changing URLs. |
Securing the Application After the Assessment
After identifying and exploiting these vulnerabilities, the ethical hacker gave the company a detailed report outlining the issues and their potential impact. The report also offered the following recommendations to secure the application:
- Use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection.
- Validate and sanitize input data to mitigate XSS.
- Implement appropriate access controls to avoid IDOR.
Conclusion: Regular vulnerability assessments of web applications, especially those that handle personal data, are important. Promptly identifying and remediating vulnerabilities is critical to protecting against potential cyber threats and ensuring the network security and integrity of customer data.
Ethical Hacking 4: Breaching Wireless Security

Scenario Overview
In this case study, a large retail company hired an ethical hacker to assess the security of its wireless network after concerns about unauthorized access. The company relied heavily on its wireless network for point of sale (POS) systems and inventory management, making the network a critical component of its day-to-day operations.
Objective: To identify any vulnerabilities in the wireless network that attackers could exploit for network hacking, as well as provide recommendations for securing the wireless network.
Wireless Hacking Techniques
During the wireless security system assessment to discover accessible networks and identify any weaknesses in their configurations, the following ethical hacking tools were used: Kismet and Airodump-ng. The ethical hacker identified the following wireless security breaches:
- The company was using outdated encryption protocols (WEP) for some of its access points, which were easily hacked.
- By sniffing packets from a wireless network, it is possible to successfully crack WEP encryption and gain access to the network, intercepting data, including sensitive information, transmitted between POS systems and company servers.
- Poorly configured access points with weak passwords further undermine network security.
Steps to Secure Wireless Networks
After demonstrating the vulnerabilities, the ethical hacker gave the company a detailed report highlighting the risks associated with outdated encryption protocols and weak access point configurations. To secure the wireless network, the following steps were recommended:
- Upgrade encryption to WPA3: To prevent network traffic from being easily decrypted, replace WEP with WPA3, the latest and most secure wireless encryption standard.
- Harden access point configurations: To minimize attack vectors, reconfigure all wireless access points with strong complex passwords and disable unused access points.
- Implement network segmentation: Segment critical systems such as POS devices into separate VLANs with strict access controls to limit potential damage in the event of a breach.
- Regular security audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration tests to ensure the network is always secure and compliant with industry standards.
Conclusion: Modern encryption protocols and robust security practices are important for wireless networks. By addressing these vulnerabilities, a company can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and ensure the security of sensitive data transmitted over its wireless infrastructure.
Ethical Hacking 5: Detecting Insider Threats

Scenario Overview
In this case, a financial institution engaged an ethical hacker to address its insider threat issues. The company was experiencing several suspicious activities, including unauthorized access to sensitive customer data and unexplained financial transactions.
Objective: Identify any insider threats or vulnerabilities in the organization’s internal security controls and recommend strategies to effectively monitor and respond to such threats.
Monitoring and Response Strategies
The ethical hacker began by implementing advanced monitoring ethical hacking tools and strategies to detect unusual activity on the network:
- SIEM
Using Security information and event management (SIEM) systems, the hacker set up real-time alerts for unauthorized access attempts, unusual file transfers, and abnormal behavior patterns. The SIEM system was configured to aggregate and analyze logs from multiple sources, including network devices, servers, and user workstations, to provide a comprehensive view of potential threats.
- RBAC
The ethical hacker also thoroughly audited user access controls, identifying instances where employees were accessing sensitive information outside their job descriptions. The audit identified multiple accounts with elevated privileges being misused to access sensitive data. The hacker then implemented strict Role Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure that employees could only access the information required for their roles.
- UEBA
In response to the identified threats, the ethical hacker recommended implementing User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) tools to monitor user activity for deviations from normal behavior. This approach allowed the company to proactively detect and respond to potential insider threats.
Lessons Learned and Preventive Measures
The Insider Threat Detection Study highlighted several key points:
- Continuous monitoring and real-time alerting are essential to detect insider threats before they cause significant damage.
- Regular user privilege audits are needed to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Implementing strong access controls and behavioral analytics to mitigate insider threats is essential.
As a preventive measure, the company has developed a robust insider threat program:
- Regularly training employees on security best practices and the implications of insider threats
- Instituting periodic audits of access control and monitoring systems to ensure their effectiveness over time.
Conclusion: Access monitoring and control are essential in detecting and preventing insider threats, which can be among the most challenging cybersecurity risks. By implementing these strategies, an organization can significantly reduce the risk of insider threat incidents and strengthen its overall security posture.
Get the most out of your budget with our affordable, efficient VPS solutions. Fast NVMe, 30+ countries, managed and unmanaged VPS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ethical hacking is vital in today’s cybersecurity world, providing organizations with the tools and expertise needed to protect against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. As cyber risks continue to evolve, the role of ethical hacking will only become more critical. We hope the real-life examples and case studies of ethical hacking in this article have helped you understand how ethical hackers discover vulnerabilities, strengthen defenses, and improve overall security. By staying up-to-date with the latest techniques and regularly testing your systems, you can better protect your digital assets and maintain a robust defense against potential attacks.
VPS for Ethical Hacking
Choose the suitable configuration and enjoy all the benefits of a virtual private server.
From $5.00/mo- Understanding Ethical Hacking
- Ethical Hacking 1: Penetration Testing of a Corporate Network
- Ethical Hacking 2: Simulating a Social Engineering Attack
- Ethical Hacking 3: Assessing Web Application Vulnerabilities
- Ethical Hacking 4: Breaching Wireless Security
- Ethical Hacking 5: Detecting Insider Threats
- Conclusion