Sometimes, situations arise where you need to change your mode of working. For example, during the COVID pandemic, many companies had to switch to remote work. The remote format of work is massively growing, exacerbating the problems of remote work security. For most companies faced with this problem, the first step is to prioritize security for remote workers and ensure proper protection. In this article, we will give some recommendations for securing remote workers.
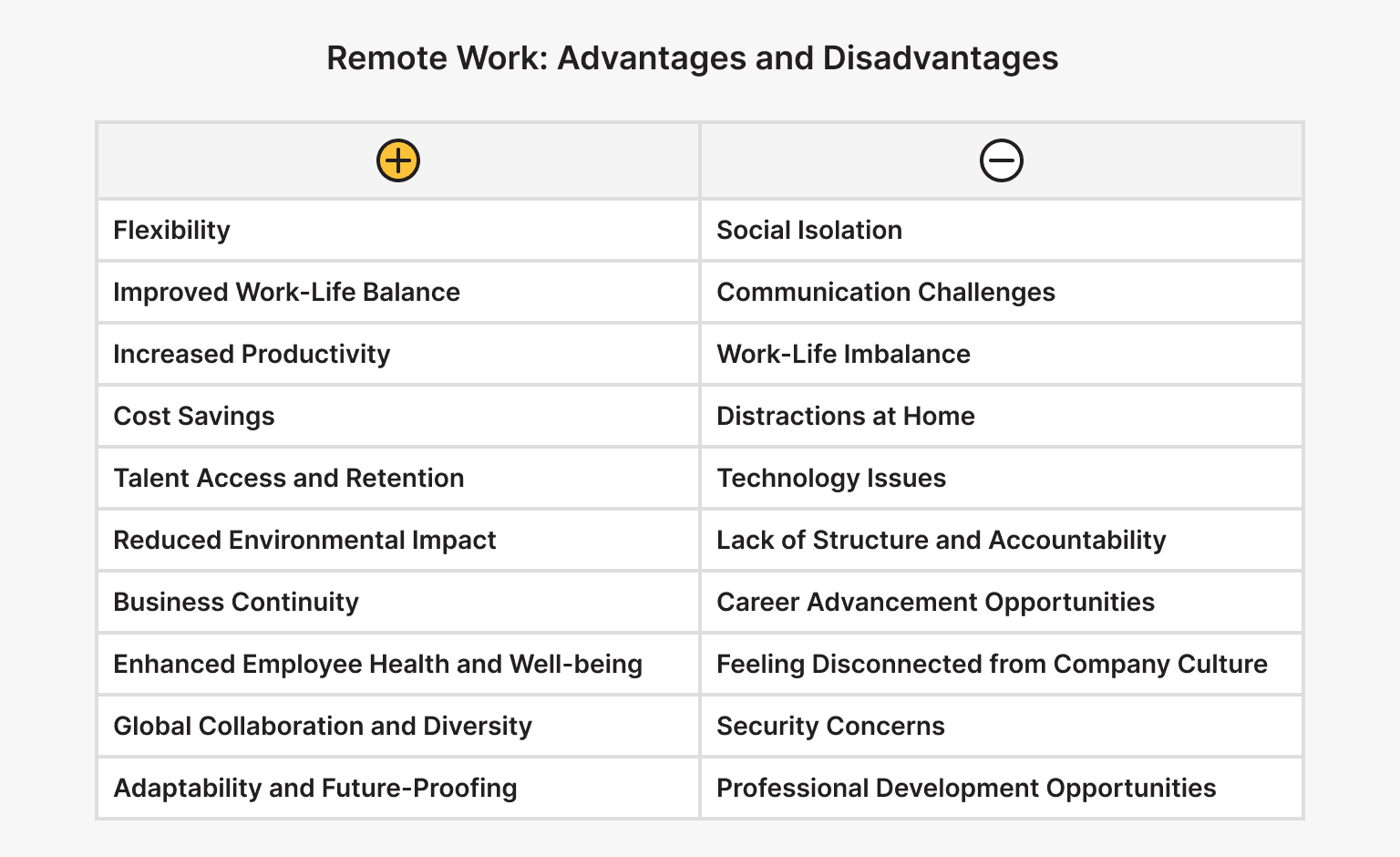
Remote Work: Advantages and Disadvantages
Recently, remote work, or flexplace as it is also called, has become increasingly popular, and because of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is also a necessity. Besides the opportunity to work with employees from all over the world from home, remote work has many advantages and disadvantages.
Remote Work Benefits
Remote work has given us freedom of action and the opportunity to work from anywhere in the world and live a better lifestyle. Remote work offers numerous benefits for both employees and employers. Some of the key advantages include:
- Flexibility.
Remote work offers flexibility in terms of when and where work is performed. Employees can often choose their ideal schedules and work from locations that suit their needs, whether it's from home, a coffee shop, or while traveling.
- Improved Work-Life Balance.
Remote work can contribute to a better work-life balance by eliminating the need for commuting and providing more time for personal activities, hobbies, and family.
- Increased Productivity.
Many remote workers report higher productivity levels due to fewer distractions and interruptions found in traditional office environments. Additionally, the ability to work during peak productivity hours, regardless of the standard 9-5 schedule, can lead to enhanced efficiency.
- Cost Savings.
Remote work can result in significant cost savings for both employees and employers. Employees save money on commuting expenses, work attire, and meals, while employers can reduce overhead costs associated with office space, utilities, and supplies.
- Talent Access and Retention.
Remote work allows companies to access a wider talent pool by hiring employees regardless of their geographical location. This can lead to a more diverse and inclusive workforce. Additionally, offering remote work options can increase employee satisfaction and retention rates.
- Reduced Environmental Impact.
With fewer employees commuting to a central office, remote work can help reduce carbon emissions and alleviate traffic congestion. Additionally, it contributes to a smaller environmental footprint by reducing the need for office-related resources and energy consumption.
- Business Continuity.
Remote work protects against disruptions such as inclement weather, natural disasters, or public health emergencies. Companies with remote work capabilities can maintain business operations and continuity even when faced with unexpected challenges.
- Enhanced Employee Health and Well-being.
Remote work can improve employee health and well-being by reducing the stress associated with commuting, providing a more comfortable and personalized work environment, and allowing for greater flexibility in managing personal and family responsibilities.
- Global Collaboration and Diversity.
Remote work encourages collaboration among teams in different geographic regions and time zones, fostering a global mindset and diversity of thought. This can lead to increased innovation and creativity within organizations.
- Adaptability and Future-Proofing.
Remote work has become increasingly important in today's rapidly changing work landscape. Companies that embrace remote work are better positioned to adapt to evolving trends, technological advancements, and workforce preferences, making them more resilient and future-proof.
Reliable storage for backups of your project or personal use. is*hosting guarantees data protection.
Remote Work Negative Aspects
While some praise remote work and enjoy the benefits of this work format, others sincerely dislike it. While remote work offers numerous benefits, it also comes with some challenges and negative aspects. These may include:
- Social Isolation.
Working remotely can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation, especially for individuals who thrive on social interaction. Remote workers may miss out on the camaraderie and collaboration of being physically present in an office environment.
- Communication Challenges.
Remote work can hinder communication and collaboration, mainly when relying solely on digital communication tools. Misunderstandings may occur, and critical non-verbal cues may be lost, leading to communication gaps and decreased productivity.
- Work-Life Imbalance.
While remote work offers flexibility, it can also blur the boundaries between work and personal life. Without clear separation between workspaces and relaxation areas, remote workers may find it challenging to disconnect from work, leading to burnout and decreased well-being.
- Distractions at Home.
Remote workers may face distractions at home that they wouldn't encounter in a traditional office setting. These distractions can include household chores, family responsibilities, pets, and noisy neighbors, all of which can impact concentration and productivity.
- Technology Issues.
Reliance on technology for remote work means that technical issues such as internet outages, software glitches, and hardware malfunctions can disrupt workflow and cause frustration for remote workers.
- Lack of Structure and Accountability.
Some individuals may struggle with self-discipline and time management when working remotely. Without the structure and oversight provided by a traditional office environment, remote workers may find it challenging to stay focused and motivated.
- Career Advancement Opportunities.
Remote workers may have limited access to networking and career advancement opportunities compared to their in-office counterparts. Remote employees may miss out on face-to-face interactions with colleagues and supervisors, which can impact their visibility within the organization.
- Feeling Disconnected from Company Culture.
Remote workers may feel disconnected from their company's culture and values, especially if they cannot participate in in-person events, team-building activities, or company-wide meetings.
- Security Concerns.
Remote work introduces security risks related to using personal devices, unsecured networks, and potential data breaches. Without proper security measures, remote workers may inadvertently expose sensitive company information to cyber threats.
- Professional Development Opportunities.
Remote workers may have limited access to professional development opportunities such as training programs, workshops, and mentorship opportunities. These limitations can impact their skill development and career growth in the long term.
Remote Work Security Best Practices
What is remote work security? Working from home comes with cyber risks. Remote workers are often the first to encounter security threats, and they are often the source of network security incidents that can quickly spread throughout the organization.
When working remotely, employees use personal devices outside the secure corporate network, making them more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Preferably for remote work security, the working device (computer, mobile phone, tablet) is used separately, or even better, it is provided by the company with all the required (OS, software, security features, etc.). However, not all organizations can provide an employee with a corporate device when working remotely because of various circumstances. Here, the employee has no choice but to work on their personal PC, which entails many known risks. There are several comprehensive solutions for remote workers.
Implementing Strong Authentication Methods
Regarding strong authentication methods, the first things that come to mind about remote work security are strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and access control. Our article on data protection in the virtual sphere explains how to implement strong authentication methods.
Protecting Wi-Fi Networks and Home Routers
Another critical factor for remote work security is securing Wi-Fi networks and home routers. By gaining access to an employee's local network, an attacker can easily gain access to important corporate data. In order to protect your network and devices from cybercriminals and security risks, you do not need to be a technical specialist. It is helpful to know how and what protection measures can be applied.
Protection measures:
- Proxy servers.
- Firewalls.
- Secure protocols.
- Network monitoring programs.
- Virtual private networks (VPN).
- Means of protection against targeted attacks.
- Protection against DDoS attacks.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems.
Device Security
Many companies struggle to protect corporate data on employee devices. Protecting personal or corporate devices on which a company employee works remotely is a mandatory factor for remote work security. Here are some ways to keep your devices safe from intruders.
Protection measures:
- Complex, strong passwords.
- Enable device encryption.
- Secure network connections.
- Two-factor authentication.
- Constant updating of OS and software.
- Timely application updates.
- Implementation of endpoint security solutions.
Using a VPN
Employees can use virtual private networks (VPNs) for increased data security and encryption. VPN technology allows you to remain anonymous, which provides additional cyber protection for remote workers. To get a guaranteed secure tunnel, it is enough to buy a VPN with a dedicated IP from a reliable hosting provider, such as is*hosting.
VPN for those who want to remain undetected online and secure their data. Dedicated IP and complete anonymity.
Data Protection
Data protection is the practice of protecting information from unauthorized access, use, or deletion. Protection measures include a set of effective solutions for remote workers and many modern technologies that must be used for remote work security to secure personal or corporate data.
Protection measures:
- Antivirus installation.
- Intrusion detection and prevention technologies usage.
- Enabling firewalls.
- Using VPN.
- Using solutions for secure storage and files sharing.
- Data backup and recovery procedures implementation.
- Confidential data encryption during transmission and storage.
- Setting security policies.
- Restricting employees’ access to information.
- Access control and management system (ACS) installation.
- Reliable authentication technologies usage.
- Awareness and training of information security employees.
Physical Security Measures
Is it possible to be 100% secure while working remotely? No, as cyberattacks are modernizing and following the progress of information technology. However, ensuring the physical security of remote workers is also important, in addition to network solutions for remote work security.
Physical security measures:
- Separating the work device from other users, the employee should not allow anyone, even family members, to use their work devices.
- Installing a “cover” on a webcam will protect the employee’s privacy if intruders gain access to the camera.
- Secure storage implementation and physical documents disposal.
- Careful handling of work equipment during transportation to avoid theft with subsequent unauthorized access to data.
Remote Work in BYOD Mode
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) is a remote work security policy that allows and encourages the use of personal devices for work tasks.
The major factor of this policy is the use of familiar equipment and solutions for remote workers, which entails an increase in employee productivity.
Obviously, from a hardware point of view, BYOD is the cheapest method, but not from a security point of view. Therefore, companies simply need to implement reliable security technologies on personal devices. Today, many large companies offer full-fledged services to support this model. BYOD is becoming an increasingly popular trend and the best alternative for remote work.
The implementation of mobile device management (MDM) solutions is also gaining popularity.
MDM is a solution that represents a digital infrastructure for managing mobile devices for remote work security. MDM includes client and server parts. The client part is installed on a mobile device and connects to the server part via a secure channel. Thus, the administrator gets access to numerous tools and can manage the mobile device in the following way:
- Installing, uninstalling, and updating applications.
- Setting restrictions and prohibitions.
- Location tracking using a tracker.
- Device remote configuration according to the company’s security policy regulations.
- Certain information and remote-blocking encryption.
All capabilities and policies of MDM solutions are aimed at preventing all kinds of incidents related to device hacking and unauthorized access to secret company data.
Awareness and Training
What are the security concerns of remote work? The world of information technology is rapidly changing and developing. All changes require the adaptation of employees. Awareness and education play an important role in remote work security. An employee who is aware of common security threats can prevent them promptly. To achieve this, it is critical to inform and train remote workers about common security threats and then train and test them to recognize and prevent phishing attacks aimed at unauthorized access to sensitive data and other social engineering threats. It is also good practice to encourage vigilance and reporting security breaches.
Security and Incident Response Policy

Particular attention is paid to developing policies and recommendations for remote work security. Every company has a different security architecture. With remote work, the concept of a perimeter that needs to be secured has become obsolete, and endpoint security has become a priority. Ensuring continuous monitoring and incident response effectively helps detect and prevent cyberattacks before they can cause real negative consequences for the company. Conducting regular safety checks and assessments will help constantly monitor the situation and dynamics.
When working remotely, special attention should be paid to incident response in case a cyberattack occurs. Incident Response (IR) is a comprehensive approach that helps IT departments prepare and develop a plan in response to IT incidents such as service interruption, a breach of an organization's security system, or a cyberattack. Effective incident response requires comprehensive incident management measures and tools to help minimize damage and downtime.
The incident response process is divided into four stages:
|
Step |
description |
|
Preparation |
Preparation is the most crucial step in incident response. It includes:
|
|
Detection and Analysis |
The actual incident response stage includes:
|
|
Containment, elimination, and recovery |
At this stage, the attacked systems are identified, and the impact consequences are localized, mitigated, and recovered as part of the IR plan.
|
|
Review (after incident analysis) |
This stage includes:
|
Conclusion
In this article, we've covered various aspects of remote work security and discussed security best practices. However, in today’s rapidly developing IT world, there are many risks associated with data loss. Therefore, we conclude that it is important not only to comply with all the security measures described above but also to conduct a correct risk analysis, constantly improve, and develop security strategies to prevent possible incidents.
Personal VPN
Stay anonymous online with a dedicated IP and don't endanger your personal data.
Get $5.00/mo