Storing large amounts of sensitive customer data, handling financial/payment transactions, and handling highly sensitive or even classified data - all add an extra layer of responsibility, as data loss means loss of reputation and profit.
With the rise of remote working, systems are often accessed from multiple locations. And the ingenuity of attackers who profit from stealing your valuable data only adds to the challenge.
Refraining from underestimating hackers' capabilities or human error can lead to data loss. We've outlined the basic steps you need to take to make your hard drive a fortress that protects everything you store on it.
How should you protect the data on a hard drive?
Physical Security Measures
Hard drives containing sensitive data should be stored in secure, locked rooms with strict access control. Only authorized personnel should have access to the server room, and monitoring entrances and exits adds another layer of protection. Overall, your company's server room should be the safest place possible, with little or no damage from flood or fire.
Another is physical media control and the ability to lock/protect removable media and portable backup devices.
For example, if your servers are located in a data center, ensure they provide 24/7 hardware monitoring, reliable cooling, and emergency response systems.
Encrypting Hard Drive Data
Whether it's an internal or external hard drive, flash drive, or HDD, encryption can be brought to the forefront of data protection non-physically. Because the encryption hardware is integrated directly into the drive controller, the drive can operate at its intended data transfer rate without impacting performance.
Encrypting the entire hard drive is best to protect all files and folders. This can be done manually using encryption software or automatically using features built into the operating system.
Although full drive encryption protects your entire system, you may need additional protection for susceptible files, such as financial records, passwords, or backups.
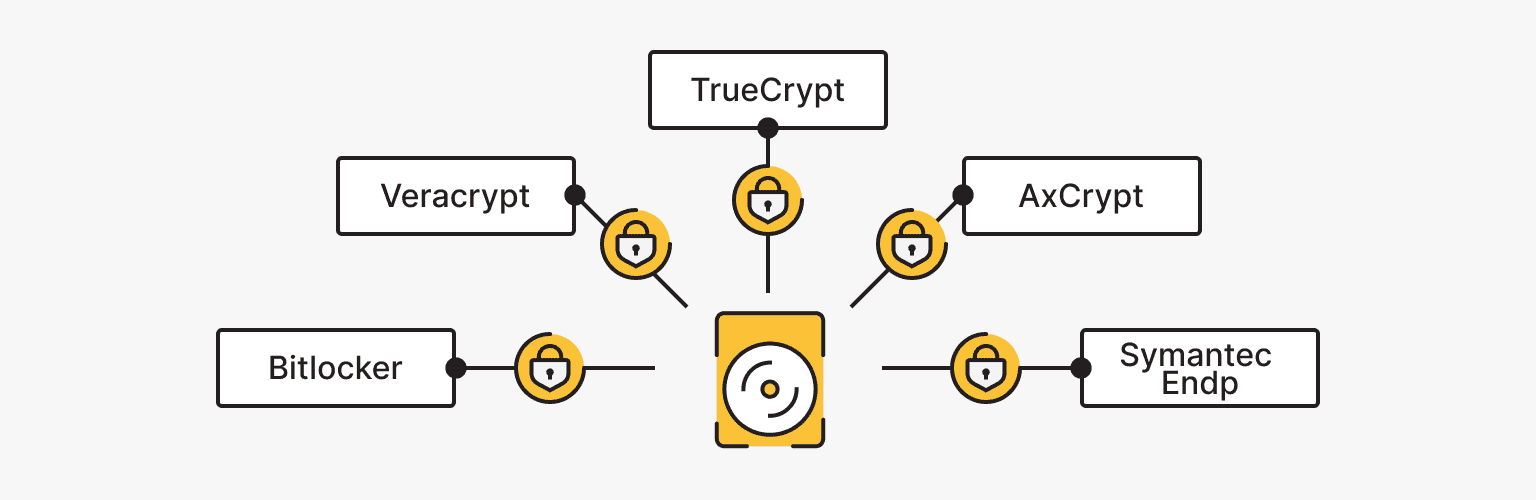
There are several programs designed to encrypt hard drives:
- Bitlocker
- Veracrypt
- TrueCrypt
- AxCrypt
- Symantec Endp
You should also encrypt any removable or portable hard drives that may contain important documents and media files. This will protect the data even if the physical drive falls into the wrong hands. Virtual Private Servers (VPS ) have built-in full drive encryption for added security, making them a convenient and secure place to store data.
You can use the following methods to access encrypted data:
- TPM is a separate module on the motherboard that stores cryptographic keys for accessing encrypted files. If it detects changes in the operating system or attempts to access documents by other means, it automatically restricts file browsing.
- A 4-6 character PIN code.
- A USB key containing an access key must be inserted into the computer to access files.
- Traditional password.
To ensure that the encrypted data remains unchanged, use cryptographic hash functions to create a hash, or digital fingerprint, of the files before and after transmission. Any changes will cause the hash value to change. This serves as a check on the integrity of the data and the encryption of its contents.
Despite its many benefits, encryption does not protect your computer from attacks. Hackers can still infiltrate your systems through insecure network connections, malicious email links, and malware that steals usernames and passwords.
VPS
Virtual private servers - efficient operation at a favorable price. Fast NVMe, 25 countries, managed and unmanaged VPS.
Backups Policy
Hard drives are mechanical devices that will inevitably fail at some point. To protect your data from loss due to hardware failure, it is important to back up your files on a regular schedule.
|
Full backup |
Incremental backup |
Differentiated backup |
|
Creating copies of all system files. |
A full copy of the system is created, and the files that have been changed are saved to the backup. |
Saving copies of only the data that has changed since the last backup operation |
The most profitable option is to automate the process of creating backups. For example, is*hosting creates free backups of each VPS and dedicates servers to remote storage weekly and daily if necessary.
For complete data recovery, backups should be kept separate from the primary storage or server. This prevents the loss of all copies in a fire or other localized incident.
Creating a backup is only half the battle because you must perform a test restore. To ensure that backups work as they should, you should regularly restore backups in a test environment to ensure that all files, applications, and systems can be recovered.
Hard Drive Access Control
Protecting your hard drive and its sensitive data requires careful access control. One of the most important steps is to set strong passwords for access to your computer and hard drive. This article explains how to create strong passwords.
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of authentication in addition to a password, such as a code sent to an email or phone. MFA can be implemented in various ways and used for different types of access control, such as application or network access. The specific implementation of MFA depends on the sensitivity of the data or system being protected and the potential risks.
Assigning appropriate file permissions is another effective way to control access to data. Use the chmod command in Linux or the icacls command in Windows to set file permissions so only authorized people can access, edit, or delete documents.
Using the principle of least privilege (PoLP) is good practice, whereby employees are given the minimum number of privileges (access to specific parts of the system) necessary to perform their jobs.
This principle is implemented in various contexts, ranging from creating employee profiles in an internal database to programming where a process is given only the resources it needs to perform its specific function. In all cases, the goal is to reduce the likelihood of damage in the event of a system breach where the entry point is a particular employee profile.
Regularly reviewing access logs will help you detect attempts to access the drive: unusual login times, failed login attempts, access from new devices, etc.
Network Security
Firewalls are essential security tools that act as gateways, monitoring and controlling inbound and outbound network traffic. They are critical in protecting your server or network from unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and potential security breaches.
Packet filtering, port control, network address translation (NAT), and other options can significantly enhance the protection of the hard drive, network, and the entire server.
To configure the firewall correctly, note the following steps:
- Allow only necessary inbound and outbound traffic. Block everything else and configure rules to allow only traffic from specific sources/applications.
- Use separate network interfaces for external and internal traffic.
- Protect traffic between systems with VPN or encrypted tunnels.
- Enable stateful inspection to analyze sessions and connections.
- Enable signature inspection (IDS/IPS) to detect malicious traffic.
- Protect USB ports with rules that allow only specific devices.
- Allow only encrypted traffic on database-related ports.
- Regularly update firewall rules and databases as they become available.
- Monitor firewall and system logs for attacks or suspicious activity.
To monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and potential attacks, it is useful to deploy IDS/IPS. These systems can detect and block malicious traffic, including attempts to access sensitive data.
Malware Protection
Modern methods of stealing information, hacking into complex systems, and holding people for ransom are enough to scare any business owner. But antivirus programs are evolving to keep up with hackers' ingenuity. To find the right software, check out our article "Free and Paid Antivirus Protection: Best Solutions Review."
In this case, you can provide real-time monitoring and threat detection. Regular checks and scans prevent problems and identify security bottlenecks on your server.
You can also use antivirus software to scan new files before you open them. Whether it's a file from an e-mail or a collaboration document from a third-party drive, you can check it for malware.
Another step in monitoring your hard drive is to use tools to check its health. Here are some options available today for various operating systems:
- Stellar Drive Monitor.
- HDDScan.
- Smartd.
- Hard drive Sentinel.
RAID (data redundancy) and replication
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent drives) is a storage technology that combines multiple physical drives into a single logical unit. It provides increased data reliability, improved performance, and fault tolerance.
What is the difference between this technology and simple data storage?
- You create a RAID array consisting of multiple hard drives.
- One of the drives fails, and you are notified of the failure.
- You replace the drive, and the RAID array recovers the lost data on the new drive.
- After some recovery time, you can use the array again.
Data recovery in RAID is accomplished through data redundancy. If you save a single 1 GB file, RAID will store that gigabyte somewhat redundantly, creating multiple fragmented copies of that file on other drives.
This technology has several implementations, but a common one is RAID5. Three drives are used for storage: each file is split into two parts and written to two drives, and additional information is written to the third drive; the same tactic is used for the following file. If one of the drives fails, a particular algorithm can recover all the files from the two remaining drives.
An alternative option for distributed storage is geo-replication between multiple servers, such as in different data centers.
A data replication strategy that copies data across multiple geographically dispersed data centers improves data availability, disaster recovery, and performance by storing copies in different locations. With replication, changes made to one copy of an object can be propagated to other copies.
What else to consider when protecting your hard drive?

Robust access controls, proper firewall configuration, traffic control, encryption, and physical security measures help ensure that only authorized users and applications can read or modify data, protecting information from external and internal threats.
Regular monitoring and logging help you detect suspicious access early. System auditing also keeps your security measures "up to date" and allows you to take timely corrective action.
The only thing we should have mentioned in the article is human error. Many data have been irretrievably lost because of downloading a file from a trap email, accidentally deleting the root folder, or not being aware of the necessary security measures.
You can quickly lose important data through carelessness or ignorance, confirming the importance of creating all the conditions to recover files or restrict access quickly.
Dedicated Server
Smooth operation, high performance, and user-friendly setup - it's all there for you.
From $70.00/mo