Every team has that one folder — the one packed with credentials, client contracts, or internal docs that should never end up outside your infrastructure. That’s where file protection and copy protection stop being abstract policies.
At its core, file protection mechanisms start with access control. Controlling who can access your sensitive files, how they’re shared, and what happens when someone moves them off approved systems. Without that control, you’re one sync error or ex-employee away from unauthorized distribution or data loss.
Let’s go beyond “do not copy” labels and look at what real-world file protection looks like for teams, including copy protection software and preventing access for unauthorized users.
How to Copy-Protect Microsoft Word Documents

Let’s be honest, Microsoft Word isn’t exactly where you expect to handle mission-critical data. Yet it still happens: project proposals, investor decks, compliance reports, and sometimes even code documentation end up in .docx form. That’s why understanding the basics of file protection here matters — it’s often your first (and weakest) line of defense against unauthorized distribution.
Using Word's Built-in File Protection Features
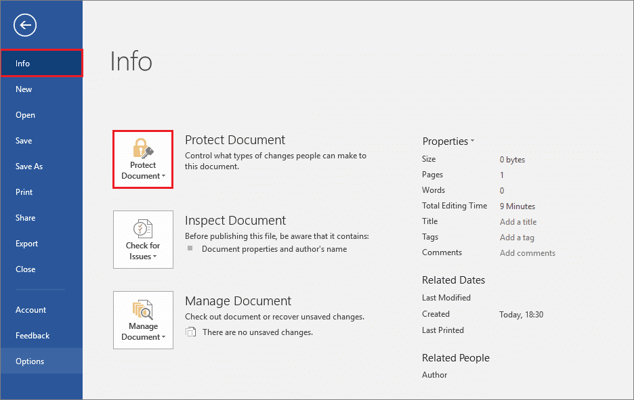
Word actually has several mechanisms to copy-protect documents, which help reduce risk when sharing sensitive files internally or with partners. They won’t replace encryption or multi-factor authentication, but they can stop someone from accidentally (or intentionally) modifying or copying your content.
You’ll find these under File → Info → Protect Document, where you can:
- Mark the document as Read-Only so recipients must opt-in to editing.
- Encrypt with Password (use something better than “1234”).
- Restrict Editing to specific roles or sections.
- Add a Digital Signature to confirm integrity.
- Mark the document as Final, signaling it’s no longer up for edits.
It’s basic document security, but it helps close the easy leaks.
Prohibiting Editing of Text
If your team needs stricter copy protection, Word lets you define exactly what can be changed:
- After following the steps in the previous section, select Restrict Editing from the drop-down menu in the Protect Document tab.
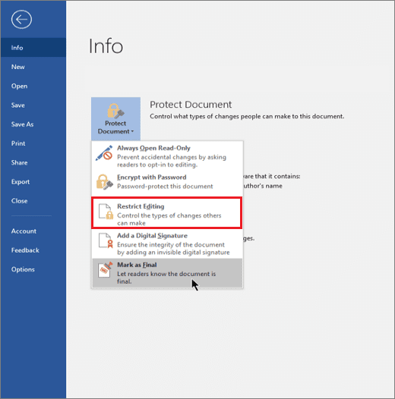
- You can also select Restrict Formatting and Editing on the toolbar in the Review tab.
- A sidebar will appear on the right side of the document, where you can select the Restrict Formatting and Editing feature and configure it appropriately in the resulting settings window.

- Also, you can select the Editing Restrictions function > Allow a specified editing type and choose it from the methods offered.
- Below, you can highlight parts of the document and determine who can edit them.
- To enable protection, click the Yes, Start Enforcing Protection button.
- You can turn off these settings later.
- Restricting Copying the Text
There are two approaches: what actually deters copying vs. a visual deterrent. The first limits editing capabilities, while the second simply visually indicates authorship.
4 Steps to Prohibit Copying Factually
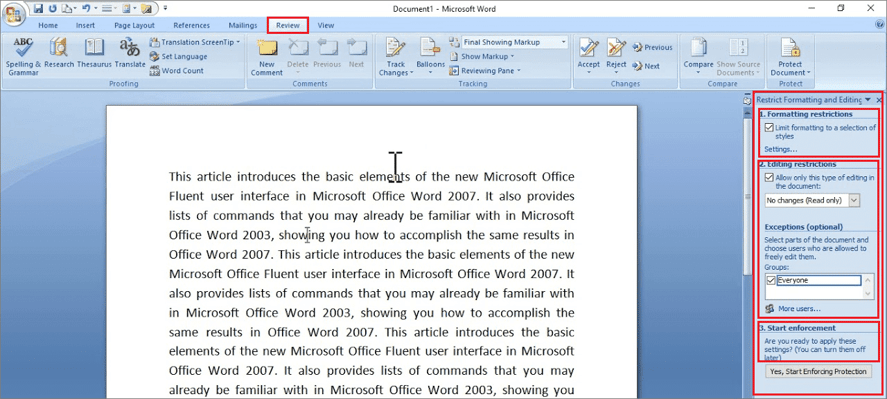
- Open the Restrict Formatting and Editing side window.
- In the Formatting restrictions item, select the Limit formatting to a selection of styles function.
- In the Editing restrictions item, allow the specific editing type.
- Click Yes.
4 Steps to Prohibit Copying Formally
- Set the background in the Design tab > Watermark.

- Open the Editing Restrictions side window.
- In the Formatting restrictions item, select the Limit formatting to a selection of styles function.
- In the Editing restrictions item, enable the editing type Read-only.
- Setting a Password for File Protection
Although it's not multi-factor authentication, a good old password can also come in handy to copy-protect documents.
Here are the steps to set the password:
- After following the steps in the previous sections, enter Protect Document and select Encrypt with Password.

- Enter the password.
- Click Ok.
Just remember: once you add restrictions, keep your password safe; Microsoft won’t recover it for you, regardless of the operating system you use.
Restricting Access to the Document
For internal documents, switch Word to Always Open Read-Only mode. It’s not encryption, but it forces intent — people must actively choose to edit, which adds friction to accidental changes or leaks.
How to enable read-only mode:
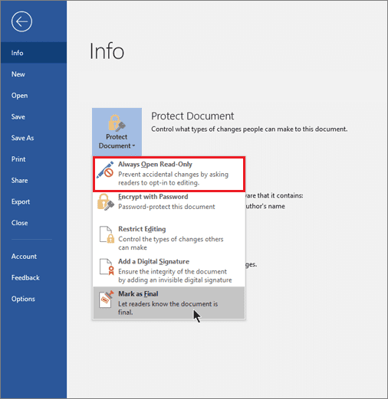
- After following the steps from the previous sections, enter the Protect Document tab.
- Select Always Open Read-Only to prevent accidental changes by asking readers to opt in to editing.
Still, if you’re working with sensitive files — contracts, credentials, product roadmaps — it’s smarter to control access at the infrastructure level. Hosting these files in an isolated VPS environment with encrypted file storage, like on is*hosting, lets you combine Word’s copy protection with server-side safeguards and proper multi factor authentication.
How to Ensure PDF File Protection

PDFs are the universal format for business — reports, contracts, and compliance docs travel the world in .pdf. That makes them a common target for unauthorized distribution or leaks. Proper file protection ensures that sensitive files stay encrypted, traceable, and editable only by the right people.
Setting Passwords
To copy-protect a PDF, use Adobe Acrobat’s native file protection mechanisms. You can protect a PDF with a user password (required to open the file) and an owner password (controls editing, printing, and copying).
Note that passwords cannot be added to a signed or certified document.
4 Steps to Restrict Editing of a PDF Document
- In the All Tools panel, go to Protect a PDF.
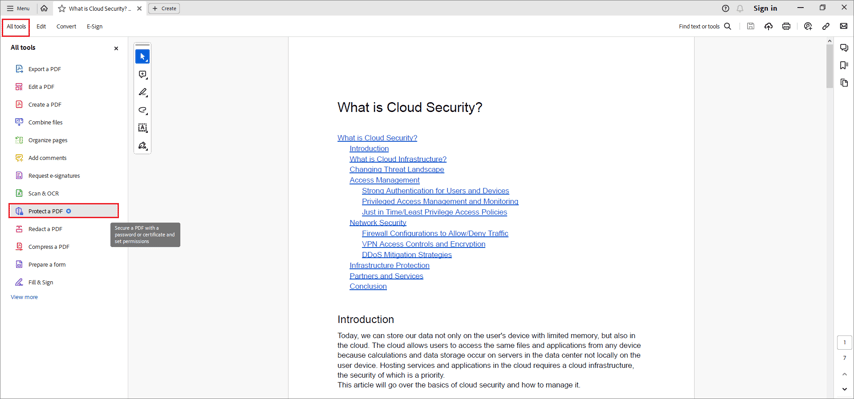
- Select Protect with password.

- In the window that opens, select the action you need, enter and confirm the password.
- Click Apply.

PDF File Protection from Copying and Printing
You can also add copy protection to stop unauthorized copying or printing of a PDF:
- In the same All Tools panel, go to Protect a PDF.
- Select Encrypt with Password.
.png?width=566&height=400&name=12-pdf-file-saved-en.png.img%20(1).png)
- When prompted to change your security settings, select Yes.
- Select Restrict editing and printing of the document and adjust the settings you want.
- To change the access rights settings, enter a password.
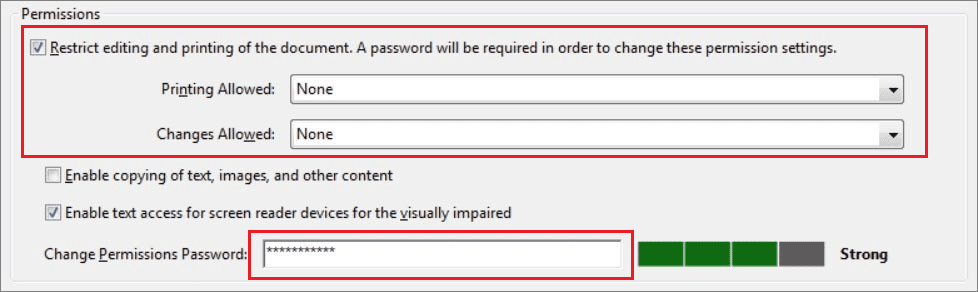
Passwords can’t be recovered — store them securely.
Advanced File Protection Options
Acrobat’s security dialog also offers granular controls:
- Allow copying or text access for accessibility devices only.
- Enable limited changes, such as commenting or signing forms.
- Choose between encryption levels (e.g., AES 128-bit or AES 256-bit).
Encrypting all document contents (not just attachments) significantly improves data security if the file leaves your network.
Dedicated Server
Dedicated hosting for those who need more power, control, and stability.
Properties of PDF Document
Viewing a PDF document helps to get information about its properties: description, title, author, fonts, security, etc.
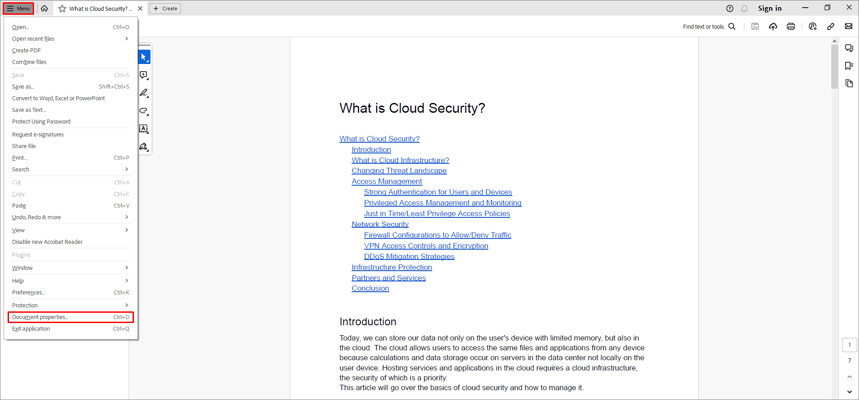
- Go to Menu.
- From the drop-down list, select Document properties.
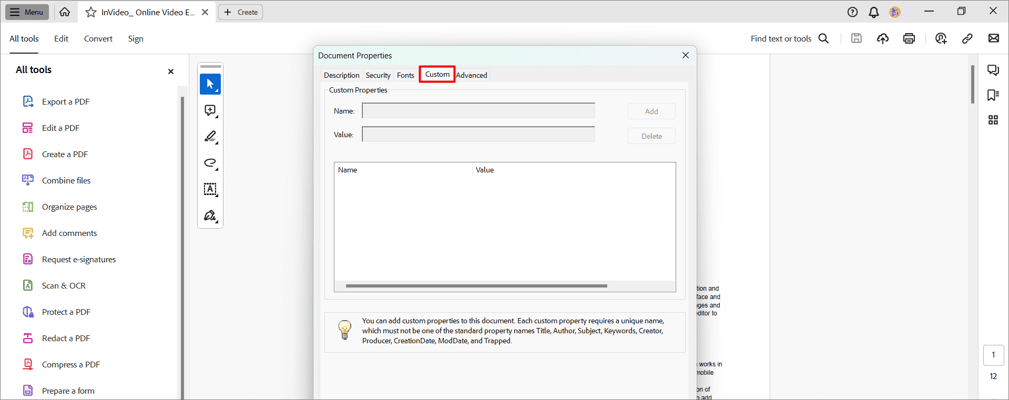
- You can change any of these properties: enter a title, subject, author, or keywords that will make it easier to find this document.

- To make the document unique, you can add custom properties in the Custom tab.
Using Certificates and Digital Signatures
For professional environments, password protection isn’t enough. Use certificate-based encryption to assign access to specific users or groups, and digital signatures to verify authenticity.
How to Encrypt a PDF Document Using a Certificate
- In the All tools panel, select Protect a PDF.
- Select Encrypt with certificate.
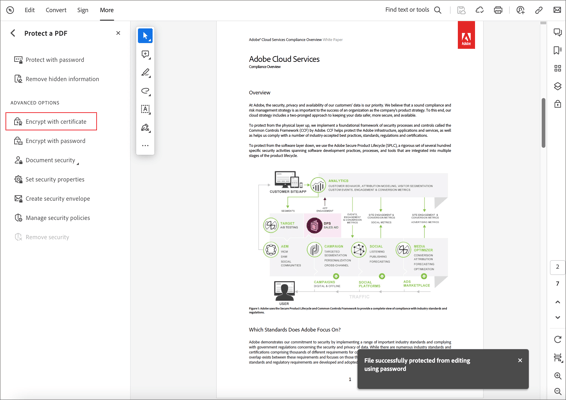
- In the Certificate protection options dialog box, select the document options you want to encrypt.
- From the Encryption algorithm menu, select the encryption level.
- Click Next.
6 Steps to Copy-Protect PDF Documents with Certificate-based Signature
Unlike a handwritten signature, a digital signature stores unique encrypted information, including credentials automatically applied to the signed document.
- All in the same All tools panel, select Use a certificate.
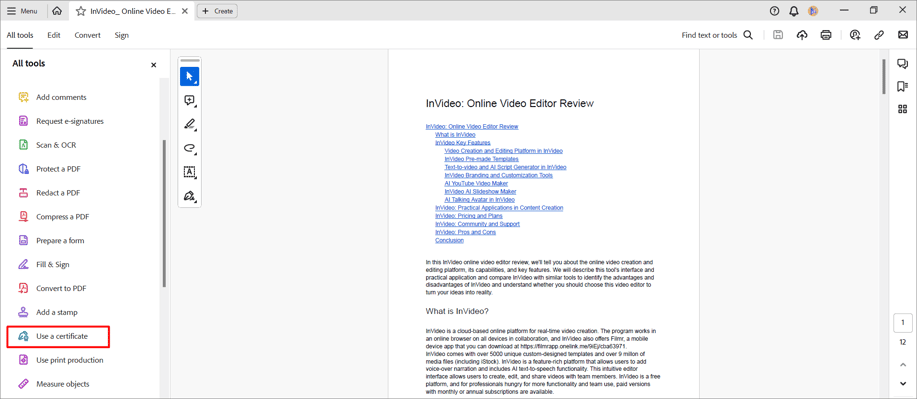
- Select Add signature or Certify (visible signature).
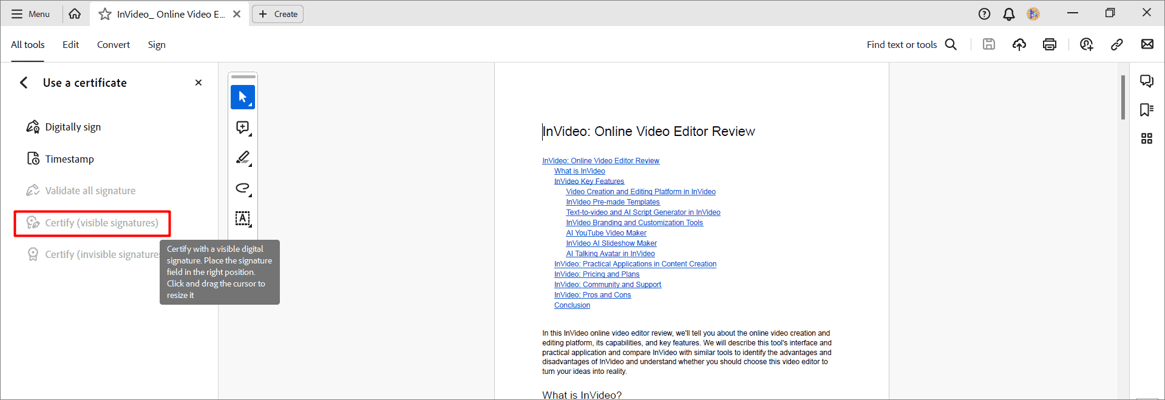
The Certify option provides a higher level of document security than the Digital Sign option. If files require certification, they must be certified before other users can sign them. If the file is already signed, the Certify options will not be available. When you certify a document, you can specify the changes that other users are allowed to make. - Enter your signature text.
- Click Apply.
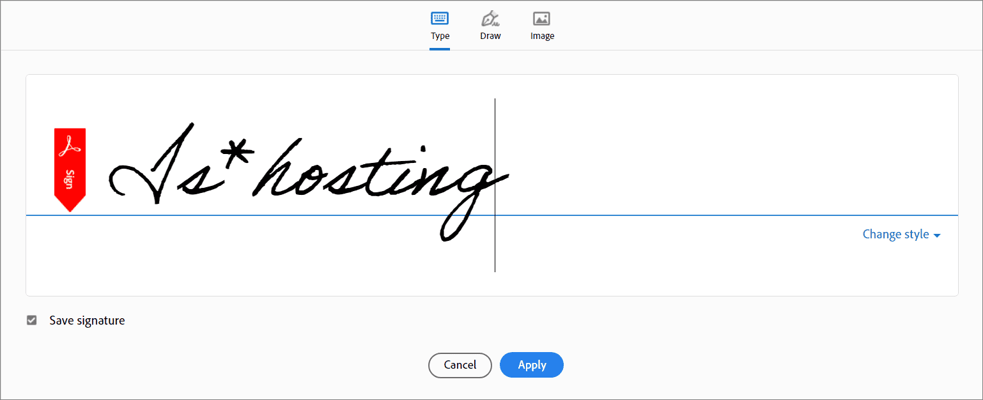
- Place the rectangle with the signature in the document in a place convenient for you.

- The signature is ready.

Digital signatures reinforce trust and authenticity — key pillars of document security in distributed teams.
How to Copy-Protect Excel Spreadsheets
Spreadsheets often hide the most sensitive files in any company — pricing models, revenue projections, customer data, even credentials buried in formulas.
Microsoft Excel includes several file protection methods that help control access, block unauthorized distribution, and ensure document security for both local and cloud-stored workbooks.
Restricting Access to Sheets
The simplest approach is to password-protect your workbook or individual sheets.
This prevents anyone from editing or even viewing content without permission — a basic but effective layer of copy protection.
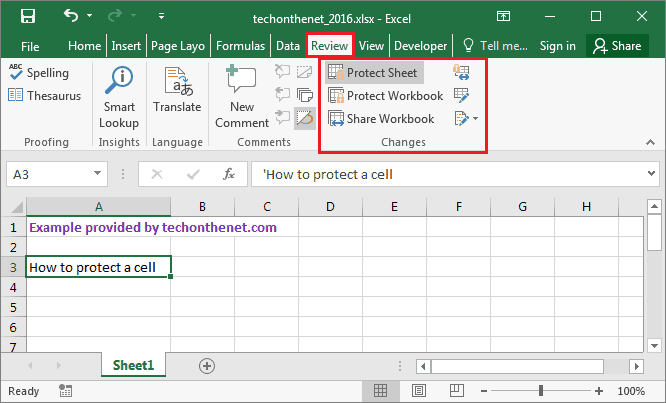
Guide to restrict access to a table:
In the Review tab, find the Changes section and select the file protection you need according to the character of the table access restriction:
- Protect Sheet if you want to place restrictions on other users’ editing rights.
- Protect Workbook if you want to restrict unwanted changes to the table structure.
- Allow Edit Ranges if you want to set password protection for ranges and select users to edit these ranges.
- Access to Book if you want to organize the simultaneous work of several users with the same book.
- Protect Workbookand Share if you want to give access to the workbook, but protect the tracking of changes with a password.
- Changes if you want to keep track of all the corrections made to the document.
Configure all parameters in the windows that open and click Ok to confirm the required file protection.
Hiding Formulas
Some sensitive files contain proprietary formulas or logic you don’t want exposed. Excel allows you to hide these without breaking the sheet.
- Select the cells you need in the table.
- First option: right-click these cells.
- Select Format Cells.
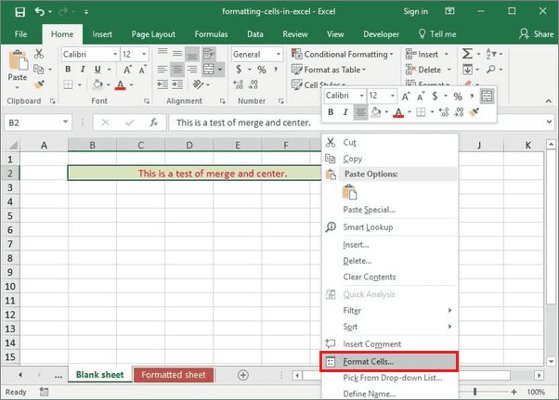
- Second option: in the Home tab, find and click Format.
- Select Format Cells from the drop-down menu.
- In the window that appears in the Protection tab, select Hidden.
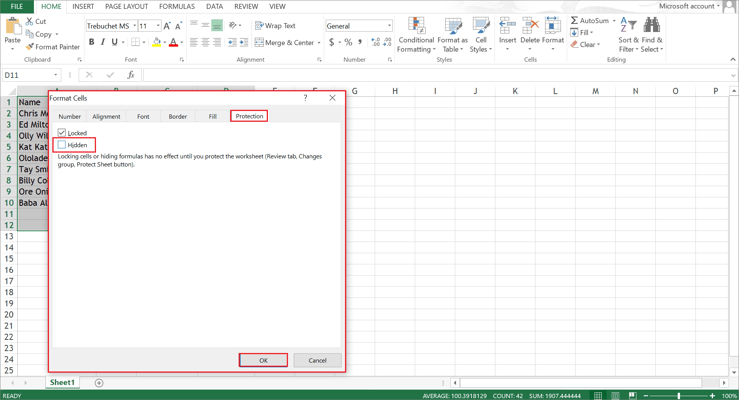
- After Protecting Sheets and setting the necessary parameters, click OK.
Locking Cells
Locking cells helps enforce file protection policies by defining which areas of a spreadsheet remain editable.
- Select the required cells.
- In the Home tab, find and click Format.
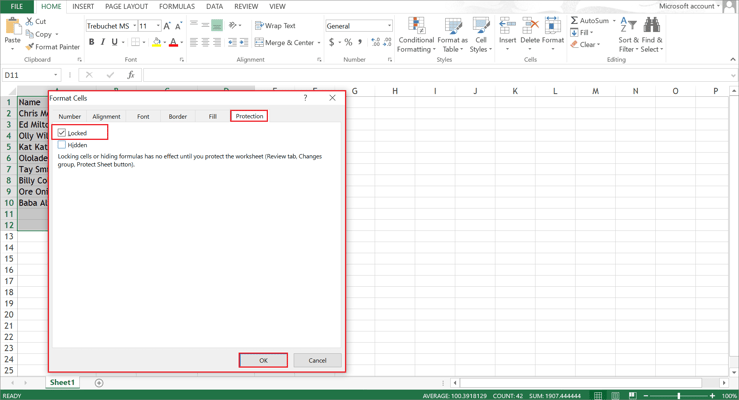
- Select Locked from the drop-down menu.
To simplify maintenance:
- Unlock any cells that will require updates before applying copy protection.
- Save a separate unprotected version for administrative use.
- Keep all credentials and unlock passwords stored securely.
How to Copy-Protect Mobile Storage Devices
Even the most advanced file protection can fail if your data ends up on an unencrypted USB disk. Portable drives and SD cards are often used for quick transfers, but they’re also weak points in your data security chain. One lost drive or misplaced backup can expose sensitive files to unauthorized distribution.
1. Using Hardware Encryption
Modern encrypted drives include built-in chips that perform on-device encryption and decryption automatically. These drives generate encryption keys internally, making it nearly impossible to access data without the correct password.
2. Using Removable Encrypted USB Drives
USB copy protection, or encrypted USB disks, is an extension of hardware encryption. They let teams enforce copy protection and maintain compliance when files need to be shared physically.
Best practices:
- Use only drives that support AES-256 hardware encryption.
- Establish a clear access policy for who can copy data and under what conditions.
- Integrate device usage into your overall data security policy — especially if your team operates across multiple operating systems.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for admin-level access if available.
3. Memory Card Encryption
Memory card encryption converts stored data into unreadable form without a decryption key. Whether you use SD cards in IoT devices, cameras, or embedded systems, it's usefull.
Key steps:
- Enable built-in encryption (BitLocker for Windows, FileVault for macOS, LUKS for Linux).
- Avoid default passwords — assign unique keys to each card.
- Back up the encryption credentials securely.
- Store backups of encrypted cards in an isolated, encrypted environment — ideally on a virtual private server with file protection at the storage layer.
Other Methods of File Protection Against Unauthorized Access and Copying

Even small oversights in how data is stored, transmitted, or accessed can lead to a loss. Below are several complementary methods that strengthen copy protection and help maintain integrity across your operating systems and workflows.
Digital Watermarks (DWM)
Digital watermarks are a subtle but effective layer of document security and digital rights management — especially for media files, presentations, or internal files that circulate across teams. They embed ownership metadata directly into a file (visible or invisible), identifying the author or source.
Information Security Software
Beyond built-in OS features, specialized software can monitor, detect, and prevent unauthorized access to protected data.
- Bitwarden or 1Password Business — for secure password and passkey management, MFA, and shared team vaults.
- ESET Protect, CrowdStrike Falcon, or Microsoft Defender for Business — for lightweight Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and threat containment.
- VeraCrypt or AxCrypt — for strong local file and disk encryption (to copy protect data at rest).
- Trellix DLP (ex-McAfee) or Safetica NXT — for Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and monitoring sensitive information exfiltration.
- Acronis Cyber Protect or Backblaze Business — for encrypted backups, rapid disaster recovery, and integrated anti-ransomware.
Firewalls, Proxy Servers, and VPNs
Network-level protection is just as important as local file defenses.
- A firewall filters incoming and outgoing connections, keeping unwanted traffic away from your private infrastructure.
- A proxy server isolates user activity and blocks direct exposure of confidential documents to external networks.
- A VPN encrypts all traffic between your devices and servers, ensuring sensitive files can travel safely over public networks.
Infrastructure-Driven Copy Protection
No matter how useful local tools may be, reliability begins with where the data is physically stored. VPS from is*hosting is an example of an environment where the infrastructure itself becomes part of the protection.
Final Thoughts
Even small documents can open big security holes. A single spreadsheet or contract without proper file protection can expose critical data through unauthorized copying.
If you’ve ever wondered what is copy protection, it’s the set of tools and practices that prevent your files from being duplicated or shared without consent — from password locks to full-disk encryption. Modern copy protection software extends these defenses across cloud storage, shared drives, and even portable media with USB copy protection.
Start simple: encrypt your files, limit access, and apply effective copy protection at every stage. Combine that with secure, isolated infrastructure — like a VPS — and you’ll have a system that keeps your data safe and fully under your control.
Data Storage
Store your backups in a safe place — is*hosting takes care of the protection.
From $2.00/mo