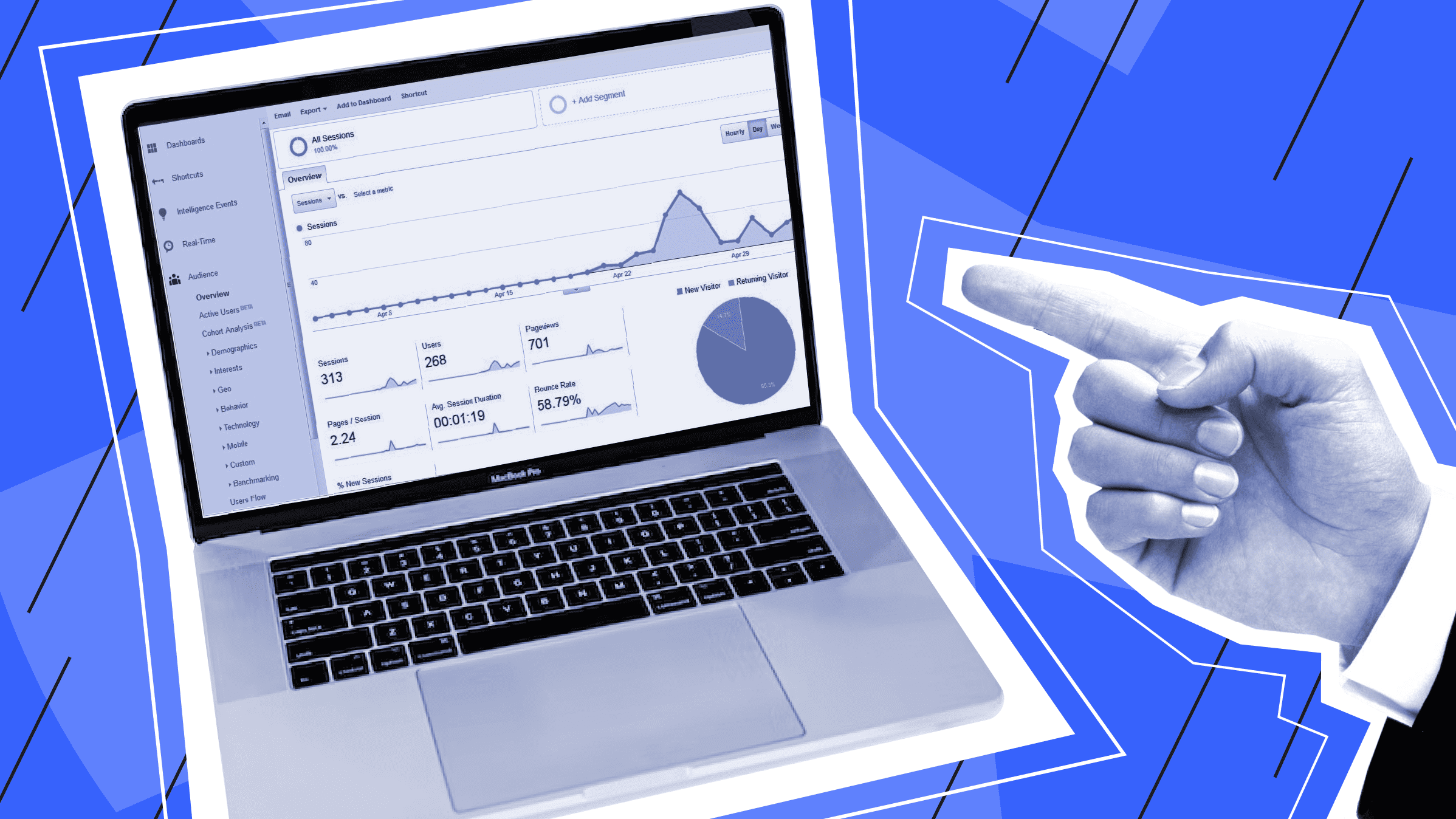
Collecting statistics and analyzing key metrics is one of the most important steps in managing a project or website. It is possible to evaluate website traffic according to different metrics, but which should be prioritized must be decided based on the goals set. It is worth noting that analyzers can also be used to evaluate the technical component of a website.
What is website traffic?
Website traffic is the number of users who visit a particular website, interact with its content and take specific actions. Website traffic is typically measured by the number of visits over a period of time or in real-time, page views, unique visitors, and other relevant metrics.
Related concepts to traffic are traffic sources, traffic metrics and trends, and metrics that can be used to determine the typical user behavior on a website. All of these concepts will be discussed below.
Why should you check your website traffic?
Among the most important objectives that can only be achieved through the collection and analysis of traffic data are the following:
- Assess the effectiveness of the website.
- Identify the website's strengths and weaknesses.
- Understand your audience, their preferences, and triggers.
- Optimize content based on audience behavior and trends.
- Track conversions by determining the number of users who complete the desired action on the site.
- Gather data to improve search engine optimization and marketing activities.
It is clear that the collection and analysis of traffic data will provide you with far more opportunities than if you were to remain in the dark.
How do website traffic checkers work?
To start tracking website traffic, you must implement the tracking code or script provided by your chosen analytical tool (e.g. Google Analytics). Typically, the tracking code should be embedded in the HTML code of your web pages. This code collects visitor data and sends it to the analytics tool's servers for processing.
Once the tracking code is in place, it starts collecting information about users' interactions with your site. This includes pages visited, link sources, time spent on each page, clicks, conversions, and more. The tracking code generates a unique identifier (usually in the form of a cookie) for each visitor, allowing you to associate their actions with a specific session.
The collected data is periodically sent to the analytics tool's servers and transmitted in the background, often using technologies such as JavaScript. The frequency of data transmission may vary depending on the specific tool and its settings.
Once the data reaches the analytics tool's servers, it is processed and analyzed. The tool consolidates, organizes, and then presents the data in easy-to-understand and informative reports and metrics. The website owner can easily obtain infographics and tips on improving the site.
The total number of visits, page views, bounce rate, conversion rate, traffic sources, user demographics, and more are just a few clicks away. Over time, if you collect enough data, you can compare similar periods and draw conclusions about seasonality or trends. It is also useful to study traffic in terms of different audience segments.
You can customize the analyzer settings to suit your needs. For example, if your primary measure of website success is the number of paid orders, set up tracking of this 'event'. This will make it easier for you to measure the achievement of a specific goal.
Different traffic analysis tools differ in functionality, flexibility of settings, and interface. It is possible to use several analyzers simultaneously if required, but the principle of operation remains the same for each provider.
Important Website Traffic Metrics to Analyze
It is equally important to know what specific metrics you need. In this case, it's traffic sources and more detailed metrics. Once you know where your site is weak, you have a goal to improve it.
Traffic to a website can come from a variety of sources, including the following:
- Direct traffic includes visitors who directly type your website URL into a browser or who bookmark your website and then click on the added link.
- Organic traffic shows users who have found your website through a search engine by typing in relevant keywords and visiting your website.
- Referral traffic is an aggregated source of traffic that comes from external links from other websites, social networks, forums, etc. However, traffic from social networks can be classified as a separate category, as SMM is an important part of the development of any project.
- Paid traffic appears in your analyzer when you run paid advertising campaigns and receive a flow of visitors from them. In this case, paid traffic is analyzed according to specific metrics.
Monitoring traffic trends over time provides valuable information about your site's performance and the effectiveness of your strategies. It helps to identify growth patterns, seasonality, and the impact of marketing campaigns or site updates. Tracking trends allows you to make data-driven decisions and adjust your tactics accordingly.

Traffic metrics include indicators of user behavior on your site, including which pages were most valuable to them and the number of people who left the site directly from the login page.
- Visits/Sessions
- Unique visitors
- Page views
- Average time on page
- Bounce rate
- Pages after which users leave the site
- New and returning visitors
- Frequency of visits
- Average time per day/day of the week visits

Conversion metrics are primarily used to track the effectiveness of campaigns and strategies and whether or not goals are being met. For example, if you are interested in the impact of an advertising campaign in terms of purchases, you should look at the return on advertising spend.
- Conversion rate
- Conversion funnels
- Average Order Value (AOV)
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA)
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
- Churn rate
- Abandoned cart rate
- Lead generation conversion rate
- Email opt-in rate

Traffic sources and SEO metrics are necessary for a general understanding of the channels through which users are coming to your site and for building strategies. If you see that traffic from social media has dropped, you know which direction to take.
- Traffic sources (direct, referral, organic, social, paid)
- Ranking by keywords
- Click-through rate (CTR) from search engine result pages (SERP)
- Backlinks (number and quality of external sites linking to your site)
- Search engine visibility (the percentage of impressions you get compared to the total number of possible impressions)

User engagement metrics allow you to focus on your audience, how they interact with your site and content, and their level of satisfaction while on your site. Based on this data, you can optimize not only the content but also the structure of your site.
- Click-through rate (CTR) (emails, ads, call-to-action buttons)
- Engagement metrics (clicks on like and share buttons, comments, social media interactions)
- Social media reach (number of unique users seeing your content on social networks)
- Customer satisfaction metrics (Net Promoter Score, customer surveys, reviews)
- Scroll depth (how far users scroll through your pages)
- Heat maps (a visual representation of user interaction and behavior on your site)

Technical metrics are designed to measure the technical aspects of your site's performance, including accessibility from different devices and the overall 'usability' of the site. Basically, if your site takes too long to load, you will lose more visitors.
- Page load time
- Mobile traffic metrics (visits from mobile devices, mobile conversion rate, mobile bounce rate)
- Device and browser metrics (devices and browsers used by visitors)
- Page errors (404 errors, broken links)
- Server response time
- Site speed index
- Accessibility metrics (WCAG compliance, screen reader compatibility)
The choice of metrics and their prioritization depends on the specifics of your site, your goals, and your strategy. Choose metrics that provide meaningful data for tracking the effectiveness and optimization of your site. Also, remember that some metrics are complex and may fall into two or more categories.
Best tools to check website traffic

Among the most popular tools for tracking and analyzing website traffic:
Google Analytics and Google Search Console are comprehensive solutions for collecting and analyzing the most important metrics.
SEMRush, SimilarWeb, Serpstat, and Ahrefs are indispensable when it comes to SEO. These tools allow you to analyze not only your site but also your competitors.
The use of dedicated analytics plugins, particularly popular on WordPress, will also be useful.
For more details on all these tools and their benefits, check out the article "Know your audience: why it is essential to collect website statistics".
What to do with the results
Identify patterns. Look for recurring trends and correlations in analytical data. Identify what is working well and what needs improvement. For example, if you notice a high bounce rate on certain pages, this may indicate a potential need to improve the content or user experience on those pages.
Make decisions based on analytical data. E.g. if certain traffic sources are generating a significant number of conversions, allocate more resources to those channels. If certain keywords are performing well in attracting traffic from organic search, then focus on optimizing content for those keywords. This includes optimizing site structure, content, and specific blocks.
Test your ideas. Use A/B or multivariate testing to experiment with different elements of your website, such as layouts, headlines, calls to action, etc. You can identify the most effective strategies by testing different ideas and evaluating them against specific metrics.
Monitor site performance regularly. Monitor performance metrics, track progress against targets, remediate weaknesses, etc. Analyze changes made and assess their impact on measurable metrics.
Share the results of your analysis with your stakeholders. You can show the analysis reports to marketing teams, web developers, or executives. Make key points, recommendations, and a plan to ensure everyone works towards the same goals.
VPS
Choose the suitable configuration and enjoy all the benefits of a virtual private server.
From $4.99/mo