Bitcoin, the world's first cryptocurrency, was described in a document published in October 2008 by an anonymous person using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. The document "Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic money system" presented a decentralized digital currency that would allow secure and direct transactions without the involvement of intermediaries such as banks.
In January 2009, the Bitcoin network was launched. This marked the beginning of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Blockchain technology is a "ledger" that stores an ever-growing list of transactions called blocks. Each block contains a set of transactions, a link to the previous block, and a unique identifier (hash). The hash of each block is created using cryptographic algorithms to ensure data integrity.
Blockchain technology enables a decentralized proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism in which network participants (miners) compete to solve complex mathematical problems to confirm and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process requires significant computing power and energy consumption.
Over the years, Bitcoin has gained popularity as a digital asset and medium of exchange. Its decentralized nature has attracted investors and enthusiasts all around the world.
However, one of the biggest challenges facing Bitcoin is scalability. The Bitcoin blockchain has a block size limit of 1MB, which means that only a limited number of transactions can be included in each block. As the cryptocurrency grew in popularity, the number of transactions exceeded the capacity of the blocks, leading to congestion and delays in transaction confirmations.
Several solutions have been proposed to solve this scalability problem. One solution is to increase the block size so that more transactions can be processed in each block. However, this approach has raised controversy and concerns about network centralization, as larger blocks require more computing resources and storage.
Another solution is to implement off-chain scaling solutions such as the Lightning Network.
Bitcoin Lightning Network Meaning
Lightning Network is a second-layer solution for scaling blockchain networks. The idea for the Lightning Network was proposed by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja and subsequently implemented for Bitcoin. The Lightning Network aims to solve the scalability problems of blockchain networks by providing fast, cheap, and scalable off-chain transactions. Is Lightning Network decentralized? Yes, it is just like the blockchain.
Lightning Network History
- 2015. A document titled "Bitcoin Lightning Network: Scalable off-chain instant payments" by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja introduces the Lightning Network concept.
- 2018. The Lightning Network attracts considerable attention. Lightning Labs, led by Elizabeth Stark, Olaoluwa Osuntokun, and others, raises $2.5 million in funding, with Jack Dorsey among the investors.
- 2019. At the end of the year, Twitter user Hodlonaut begins a promotional test of the Lightning Network in game form, sending 100,000 satoshis (0.001 bitcoin) to a trusted recipient, with each recipient adding 10,000 satoshis ($0.34 at the time) to send to the next trusted recipient.
- 2021. As the Lightning Network expands, it is increasingly supported by major cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet providers.
At the time of writing, the Lightning network has grown to 16,000+ nodes, 69,000+ channels, and total liquidity of 5,000+ BTC. Growth continues as more people worldwide learn how to send and receive fast and convenient micropayments using Lightning network applications.
How Lightning Network Works and Network Features
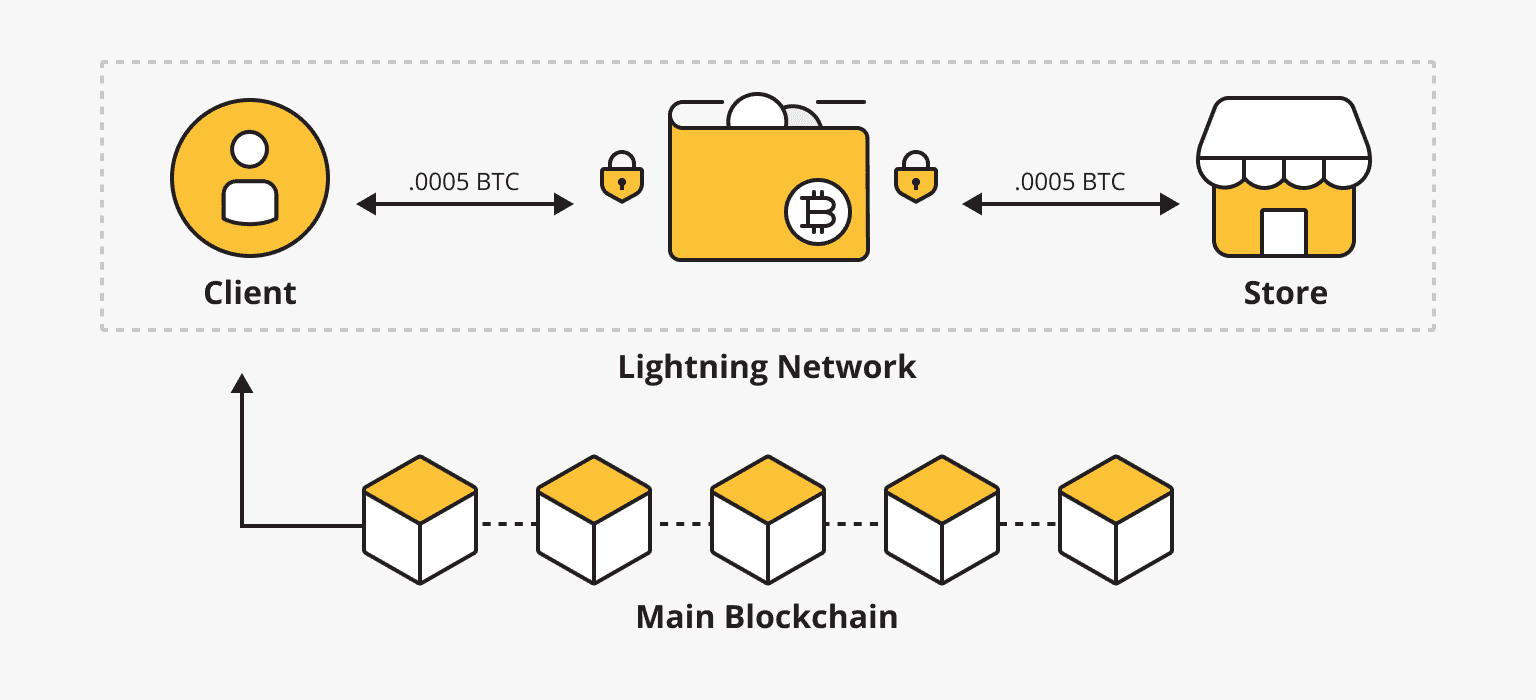
The main goal of the Lightning Network is to enable fast, scalable, and low-cost transactions by performing them off-chain. It uses a network of bi-directional payment channels established between users. These channels allow multiple transactions to occur without recording each transaction on the main blockchain.
Smart Contracts
The Lightning Network uses smart contracts to ensure the security and trustworthiness of transactions. This means that the necessary level of protection is provided during the transaction process.
It is also worth noting that LN use HTLCs, or hash-time smart contracts. These can be created using secret codes from each party involved in the payment, which are then converted into a unique hash value.
Lightning Network Workflow
The payment channel through which users can conduct transactions is a 2-of-2 MultiSig wallet. The MultiSig wallet guarantees that funds can only be used if both parties agree.
To initiate a payment channel, both parties must commit a certain amount of Bitcoins, which are held and cannot be "released" while the payment channel remains open.
LN works by establishing a payment channel between two parties with the establishment of liquidity, where only the first and last transactions are counted on the Bitcoin blockchain. Any number of transactions between the first and last will occur off-chain. Due to the lack of restrictions within the blockchain, all intermediate transactions happen much faster. Lightning network applications or wallets can be found here.
Thus, when the channel is closed, the blockchain takes into account the final state of the smart contract and only the initial transaction and the final balance of both parties.
Features of LN Operation
Based on this principle, the LN is designed to perform as follows.
- By processing transactions off-chain, the Lightning Network allows large numbers of transactions to be processed quickly without overloading the main blockchain.
- Transactions on the Lightning Network can be almost instantaneous because they do not require confirmation on the blockchain. This makes it suitable for microtransactions and everyday payments.
- The network significantly reduces transaction fees because most transactions take place off-chain. Users only pay fees when payment channels are opened or closed, and transactions are routed through intermediaries.
- LN transactions are private because there is no need to broadcast (record) each transaction on the blockchain. The details of individual payments are known only to the parties involved.
- The LN network is decentralized, making it accessible to owners of different wallets.
- For transactions taking place outside the blockchain, Lightning Network reduces the energy consumption required to run the nodes. This has a significant environmental impact, as the energy required to support these transactions is less than if they were conducted traditionally on the Bitcoin network.
Coins Using Lightning Network
Lightning Network was originally proposed as a layer two scaling solution specifically for the Bitcoin blockchain.
Ethereum, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and all other cryptocurrencies are altcoins. Many alternative Bitcoin cryptocurrencies have adopted Bitcoin's Lightning Network technology into their own networks. Lightning Labs introduced the protocol to Litecoin. Since then, the Litecoin blockchain network has experienced even faster transaction speeds and lower fees than before.
It is worth noting that there is an example of a similar solution for the Zcash cryptocurrency. Bolt Labs has developed Blind Off-chain Lightweight Transactions (BOLT), a privacy-oriented off-chain payment protocol inspired by the Lightning Network. The only downside to the implementation is the inability to verify the legitimacy of receiving and sending a transaction, which could be associated with criminal activity.
Is the Lightning Network Secure?
In terms of security, the Lightning Network has several security measures in place. For example, smart contracts ensure that transactions are executed "as intended" and that funds are only available to their rightful owners.
While the network has been extensively audited and tested, there is always a degree of risk associated with any technology.
Despite the benefits of the network, the Lightning Network is not without its shortcomings. Although the Lightning Network improves the efficiency of transactions once payment channels are created, the process of creating them is costly. Users must transfer funds to the Lightning Network and commit them to the channel, which also takes time. In addition, despite the existence of smart contracts, risks remain on the part of the counterparties involved in the chains.
The problem of counterparties and funds getting stuck in the chain because someone goes offline is solved by having watchtowers through which disputes are resolved. However, this introduces a degree of centralization into a decentralized network.
Lightning Network Use Cases
As the original idea of LN is made clear, this network enables near-instantaneous transactions with significantly lower fees than ordinary BTC transactions. This makes it suitable for everyday payments, such as purchasing goods and services, where speed and cost-effectiveness are crucial. This application of LN has been found not only in the Bitcoin blockchain and centralized exchanges (Kraken, Bitfinex, OKX, OKCoin, etc.), but also in the social network Twitter and in the state of El Salvador.
Instant and Low-Cost Payments
In 2021, Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey revealed that Bitcoin will play a role in the company's future because he believes it is necessary. Twitter lets users send and receive "tips" in Bitcoins via the Lightning Network. Through the Lightning Network-compatible payment app Strike, many Twitter users can instantly send Bitcoin payments to other Twitter accounts for free.
El Salvador has become the first country to make Bitcoin legal tender. The Chivo wallet created by the government is compatible with Lightning and is designed for seamless crypto payments. Of course, this was the starting point for popularizing cryptocurrency in the country and increasing such payments. In 2021, when the Salvadoran government announced that bitcoin would be recognized as a means of payment equal to the U.S. dollar, it also announced its intention to create an official cryptocurrency wallet to store $150 million worth of bitcoins in a trust fund based on the Development Bank of El Salvador to guarantee the ability to automatically and instantly exchange BTC for U.S. dollars.
The year 2021 was also the subject of headline news stories:
- "McDonald's in El Salvador has started selling food for Bitcoins."
- "Salvadoran authorities are giving residents Bitcoins for free."
- "Western Union's losses from the legalization of Bitcoin in El Salvador are estimated at $400 million a year."
However, this story did not have a happy ending. By the end of June 2022, the government's cryptocurrency holdings had been cut in half, and Bitcoin’s adoption in El Salvador had not gained enough traction. As a result, the government faced an acute cash shortage to make debt payments of more than 1 billion dollars in 2023. This situation is a consequence of the falling value of Bitcoin. It is worth noting that in early 2023, El Salvador began to gradually address the debt issue.
Lightning Network Zap
Zap is a popular Lightning Network wallet and application platform that provides an easy-to-use interface for managing Lightning Network channels and making payments. It offers additional features such as routing optimization, network analytics, and compatibility with various services built on top of the Lightning Network. We recently wrote an article about the decentralized social network Nostr, where you can also use Zap.
Zap allows you to connect to any of your Lightning nodes, manage multiple wallets, make on-chain and off-chain payments, view balances in Bitcoins, satoshis, and fiats, and generally manage payment channels in a convenient way.
The application is available for Windows, MacOS, and Linux and is constantly evolving thanks to its open-source code and developer community.
In addition to Zap Wallet, other solutions supporting Lightning Network are also available:
- Eclair Wallet;
- BlueWallet;
- Wallet of Satoshi.
Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps
The LN can facilitate some transactions thanks to a feature called cross-chain atomic swaps, which were first described in 2013. They allow users to exchange cryptocurrencies directly between different blockchain networks without intermediaries or centralized exchanges. Cross-chain atomic swaps have the potential to increase interoperability and facilitate decentralized trading between different cryptocurrencies, but the first practical application came much later.
Atomic swaps can operate directly between the blockchains of different cryptocurrencies and outside the blockchain. The first atomic swap exchange occurred on September 19, 2017, between Decred and Litecoin.
Atomic Swaps use a time-based hash contract (smart contract) with time-locked collateral (HTLC). This contract is time specific and involves generating a cryptographic hash function that can be verified by the parties to the swap.
This means that the HTLC smart contract requires confirmation by the recipient. Confirmation must be provided by generating a cryptographic proof of payment before the expiration date. Otherwise, the transaction is invalidated, and the funds are returned to the sender.
It should be noted that the use of Lightning Network is not a mandatory condition for exchanging cryptocurrencies via Atomic Swaps. However, LN integration will make such transactions faster and more convenient. The use of LN is best understood when transactions need to be executed off-chain.
Among the well-known implementations of atomic swaps is the BarterDEX exchange. The Komodo team stated that after successfully connecting the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains and implementing support for ERC-20 tokens, their BarterDEX exchange now supports p2p swaps between 95% of all existing coins and tokens.
In addition, the Lightning Network can be used for lending platforms, decentralized savings accounts (on DEX exchanges), and other financial services.
Criticisms of the Lightning Network
Centralization issues arise not only from the control of watchtowers but also from the existence of multiple large nodes created by organizations, leading to a kind of dominance in the network. Some people believe that such a consequence of growth could undermine the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies and potentially lead to problems such as censorship or transaction control. At this time, there is no definitive solution to this potential problem.
The availability of liquidity and bandwidth may be a limiting factor, especially for large-scale adoption or when large transactions are involved. This issue is likely related to the scalability of the Lightning Network.
Regarding user experience, there is a perception that the Lightning Network, as a second-layer solution, is more complex than traditional transactions. The network is not yet simple and convenient enough for mass adoption. Setting up and managing payment channels, finding payment routes, and maintaining sufficient channel liquidity can be challenging for users unfamiliar with technical documentation. In addition, privacy concerns still exist for LNs. It is well known that analyzing transaction patterns and network topology makes it possible to identify channel participants and recognize their behavior.
Network congestion and channel hacking are still a possibility with Lightning. If payment channels become congested and a malicious hack or attack occurs, participants may not be able to get their money fast enough, and the channel will be frozen.
The Lightning Network is not perfect and is still subject to criticism, and although it is being implemented increasingly in third-party exchange services, it needs to be improved and, to some extent, simplified. However, given the technical sophistication of avid users of cryptocurrency exchanges, this will not be a problem for them.
What is the Future of the Lightning Network?
New developments like the Lightning Network are constantly improving. And as the network has become a solution to a major problem in the Bitcoin blockchain and has become popular among cryptocurrency holders, it must evolve at a nearly seven-step pace to keep up with increasing demands for security, privacy, and usability.
The Lightning Network can benefit from protocol enhancements to the underlying blockchain, such as Schnorr signatures and Taproot. These enhancements can improve the privacy, efficiency, and security of Lightning Network transactions and provide new features and optimizations.
One of the right development vectors is also to improve the concept and implementation of watchtowers to create a more secure space for transactions and confidence in the correctness of transactions.
Several proposed extensions to the Lightning Network protocol, such as Eltoo and Channel Factories, address various scalability, usability, and liquidity issues. For example, Eltoo provides improved penalty mechanisms and simplifies channel updates, while Channel Factories enables more efficient channel creation and management. These enhancements can potentially improve the capabilities and performance of the Lightning Network.
However, the average transaction value is 0.0016 satoshi ($0.000000443), making the LN extremely viable for microtransactions and attractive to new users. The emergence of a growing number of Lightning-enabled wallets and cryptocurrency exchanges, DeFi applications, liquidity providers, non-functional tokens (NFTs), and games similar to applications on the Ethereum blockchain also play a role in the network's development.
The ability to integrate LN with other blockchains and expand functionality will take the network to a whole new level.
The Lightning Network's Impact on the Cryptocurrency Ecosystem
Lightning Labs, Joseph Poon, and Thaddeus Dryja created a layer two solution that immediately resonated with audiences.
Lightning Labs is steadily growing its ecosystem for the future, attracting investment and improving the network, and has had a significant impact on the Bitcoin blockchain ecosystem:
- One of the biggest challenges facing blockchain-based cryptocurrencies is scalability. The Lightning Network helps solve this problem by allowing users to open payment channels offline.
- Traditional blockchain transactions can be slow, especially during periods of high network congestion. With the Lightning Network, transactions can be processed immediately offline, eliminating the need for confirmation.
- By moving transactions off the Lightning Network, transaction fees are dramatically reduced. Microtransactions that were previously impractical due to high fees have become feasible and cost-effective.
- Lightning Network transactions are private and do not appear on the main blockchain.
Lightning Network Resources
Lightning Labs is one of the leading companies involved in Lightning Network development. Their website provides resources, documentation, and tools for developers interested in building Lightning Network applications. For the latest news directly from Lightning Labs, click here.
Various LN-based implementations:
- Lnd is an implementation of the Lightning Network Daemon developed by Lightning Labs. It is an open-source project available on GitHub that provides developers with a robust platform for building Lightning Network-enabled applications.
- c-lightning, another open-source implementation of the Lightning Network protocol, is developed by Blockstream. c-lightning provides a rich set of tools and libraries for Lightning Network development.
- Eclair is a Scala-based implementation of the Lightning Network by ACINQ. Eclair aims to provide an affordable and reliable platform for developers interested in building LN applications.
Lightning Network 1ML, which provides real-time information about Lightning Network nodes, links, and bandwidth, is essential. It can be used to monitor network statistics and track LN growth and adoption. Bitcoin Visuals is useful for additional statistics over time.
The Lightning Network Developer Community, presented as a collaborative platform, allows developers and other interested parties to interact, share knowledge and discuss the development of the network. You will find many useful resources, forums, and chat channels on the platform.
As an additional resource, you can use this website. There you will find guides, history, statistics, video presentations, documentation, and tools for developers.
These resources and tools can serve as a starting point for those who are interested in exploring and contributing to the Lightning Network ecosystem, both as developers and investors.
VPS
Choose the suitable configuration and enjoy all the benefits of a virtual private server.
From $4.99/moDedicated Server
Smooth operation, high performance, and user-friendly setup - it's all there for you.
From $9.99/mo